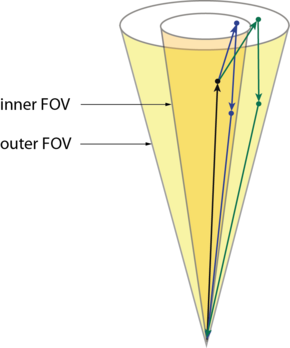
This information is exploited at dual-FOV Raman lidar measurements. At probings of clouds, the lidar return is detected with two coaxial FOVs, as displayed in Fig. 1. A forward iterative algorithm, developed at the National Academy of Sciences in Belarus within a collaboration, utilizes these signals to derive the mentioned profiles of cloud properties.
An important feature of this measurement technique is the detection of Raman scattered light in both FOVs. The exclusive detection of light which was once Raman scattered by a nitrogen molecule guarantees that the backscattering event occurs at a nitrogen molecule with an isotropic phase function, which facilitates the data analysis.