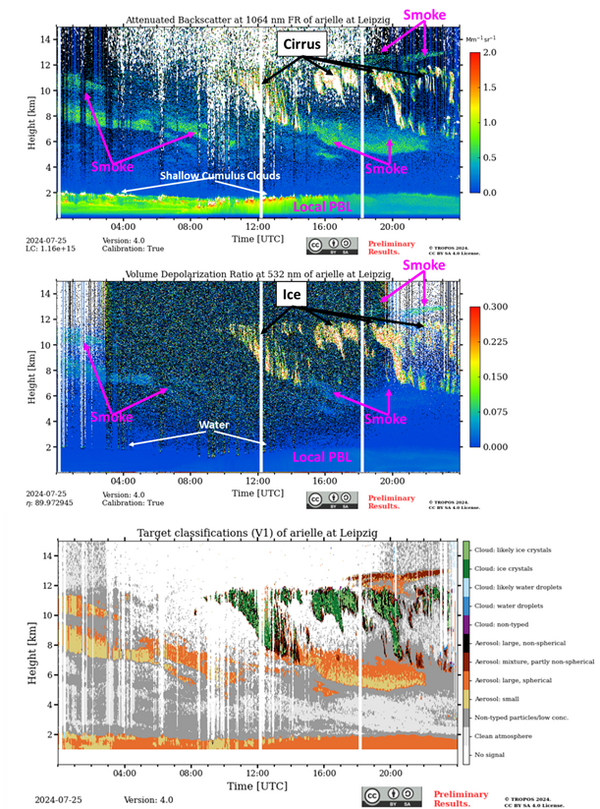
Smoky atmosphere – North American wildfire smoke influencing clouds over Leipzig
Leipzig, 31.07.2024 – Holger Baars
On 25 July 2024, strong smoke layers from wildfires in North America were observed with our PollyNET lidar over Leipzig. The smoke layers (greenish colors in the attached figure of the attenuated backscatter) extended from 4 km to 13 km above the ground and thus clearly had the potential to influence the observed ice clouds (white colors in terms of backscattering and depolarization, see figures)) which occurred on this day after 12 UTC.
The smoke did not reach the local planetary boundary layer (PBL) which was confined to the lowermost 2 km with sporadic water cloud formation (high backscatter, low depolarization in the figures).
As the smoke is only weakly depolarizing the laser light of our PollyXT (see figure of volume depolarization ratio – greenish colors) it indicates self-lofting of the smoke rather than pyroCB (wildfire-induced thunderstorms) induced lofting.
Further studies concerning smoke-cirrus-interaction with cloud radar will follow!